Unlock the secrets to eradicating fungal nail infections with our comprehensive guide. Explore the causes, symptoms, and advanced treatment options, including home remedies and preventive measures, to restore your nail health.
Introduction
Fungal nail infections, or onychomycosis, present a stubborn challenge affecting both toenails and fingernails. Triggered by an overgrowth of fungi in and around the nail area, these infections thrive in the warm, moist environments of our nails. Understanding the types of fungi responsible, including dermatophytes and yeast, and recognizing early signs are pivotal steps toward effective treatment and recovery. Dive into our expert insights to navigate the path to clear, healthy nails.
Table of Contents
Fungal Types
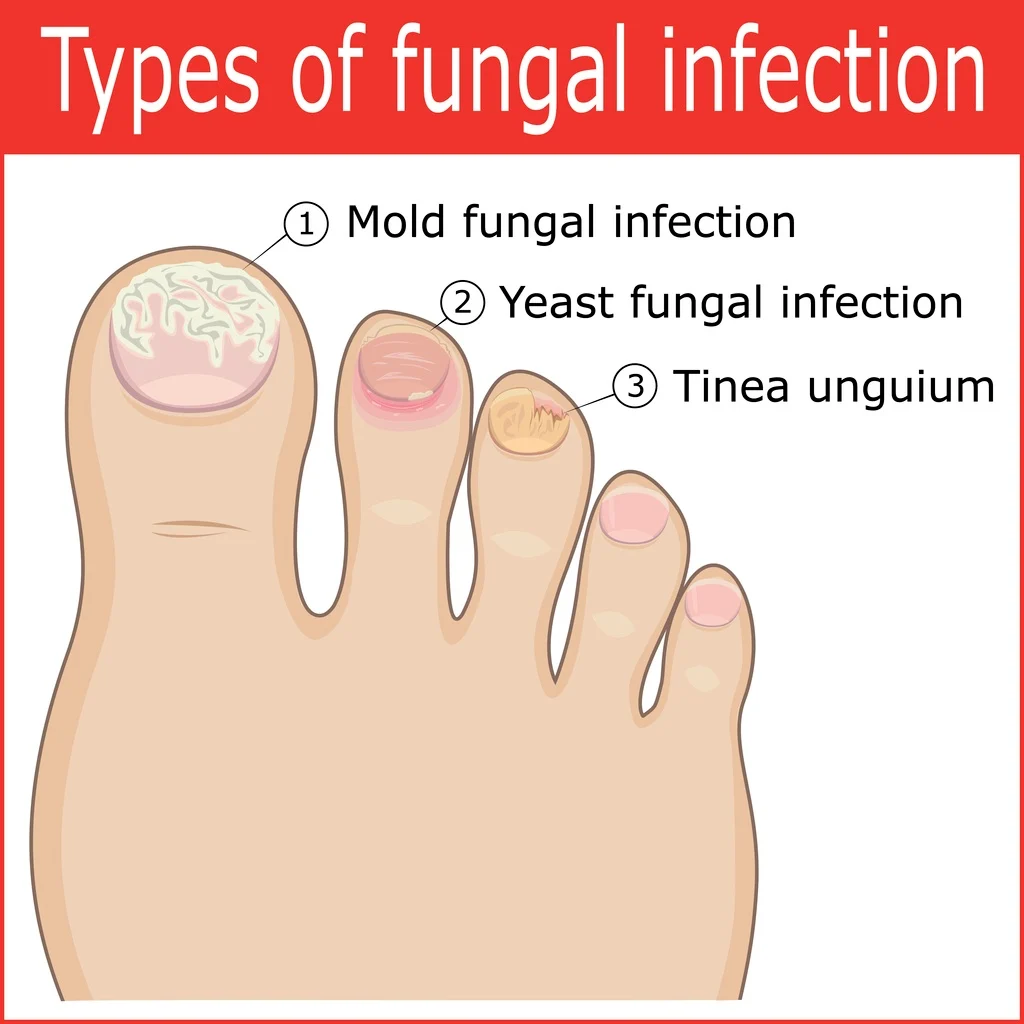
Fungal nail infections, medically known as onychomycosis, are primarily caused by three types of fungi: dermatophytes, yeasts, and molds. Each type targets the nail in different ways and may require specific treatment approaches. Understanding the differences between these fungal types is crucial for effective management and treatment. Here’s a closer look at each type:
1. Dermatophyte Infections
Dermatophytes are the most common cause of fungal nail infections. These fungi thrive on keratin, the protein found in nails, skin, and hair, which makes the nails an ideal target. The most common dermatophyte that affects the nails is Trichophyton rubrum. Dermatophyte infections typically start at the tip of the nail and gradually spread toward the base. They are more common in toenails than in fingernails.

Characteristics:
- Nails may become thickened, brittle, and discolored, often turning a yellowish or brownish hue.
- The infection can cause the nail to separate from the nail bed, a condition known as onycholysis.
2. Yeast Infections
Yeast infections of the nail, primarily caused by Candida species, are more common in fingernails but can also affect toenails. These infections are more likely to occur in individuals with a weakened immune system, those who frequently immerse their hands in water, or those with a previous injury to the nail or nail bed.

Characteristics:
- Nails may become swollen, red, and painful, with the nail plate possibly separating from the nail bed.
- The nail may appear discolored, with white, yellow, or green patches.
3. Mold Infections
Mold infections (non-dermatophyte molds) are less common and typically occur as a secondary infection following a previous injury to the nail or exposure to the fungus in a moist environment. Molds such as Scopulariopsis, Aspergillus, and Fusarium species can cause nail infections, particularly in toenails.

Characteristics:
- The nail may turn a variety of colors, including green, black, or brown.
- These infections can cause the nail to become thickened or brittle, similar to dermatophyte infections, but often with more pronounced discoloration.
Causes of Fungal Nail Infections
The development of fungal nail infections can be attributed to several factors, all of which contribute to creating an environment where fungi can thrive:
Poor Foot Hygiene
Inadequate cleaning and drying of the feet can leave them susceptible to fungal infections. Moisture and warmth are fungi’s best friends, and neglecting foot hygiene can create the perfect breeding ground for these organisms.
Tight-Fitting Shoes
Regularly wearing shoes that constrict the feet can increase the temperature and humidity around the nails. This environment is ideal for fungal growth, making tight and poorly ventilated footwear a significant risk factor.

Walking Barefoot in Public Spaces
Public areas like swimming pools, locker rooms, and showers are often wet and frequented by many people. Walking barefoot in these spaces can expose your feet to fungi, increasing the risk of developing a fungal nail infection.
Symptoms of Fungal Nail Infections
Fungal nail infections can manifest through various symptoms, which may vary in severity from person to person. Early identification of these signs is key to preventing the spread of the infection and ensuring a quicker recovery:
Yellow or White Discoloration
- One of the first signs of a fungal nail infection is often a noticeable change in nail color, with nails turning yellow or white.
Thickened Nails
- As the infection progresses, affected nails may become thicker, making them difficult to trim and sometimes uncomfortable inside shoes.
Brittle or Crumbly Texture
- Infected nails can become brittle, breaking easily, or crumbly, with pieces of the nail coming off.
Distorted Nail Shape
- The shape of the nail may change, becoming irregular or distorted as the infection takes hold.
Foul Odor
- A noticeable foul odor emanating from the nails is a common symptom of a fungal infection.
Nail Separation from the Nail Bed
- In more severe cases, the nail may separate from the underlying nail bed, a condition known as onycholysis, which can cause discomfort and pain.
Diagnosing Fungal Nail Infections
Accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment. Healthcare professionals typically employ a combination of methods to confirm the presence of a fungal nail infection:
Visual Examination
Initially, a doctor will examine the nails for visible indicators of a fungal infection, such as discoloration, thickening, or distortion of the nail.
Microscopic Examination
To identify the specific fungus responsible, a small sample of the nail may be collected and examined under a microscope. This step is essential for tailoring the treatment to the type of fungal infection.
Culture Test
For a more detailed analysis, a culture test might be performed. This involves cultivating a sample of the nail in a lab to observe the growth of the fungus, providing further insights into the most effective treatment methods.
Comprehensive Treatment Options for Fungal nail infections
Fungal nail infections, a common yet troublesome condition, demand a nuanced approach to treatment that considers the infection’s severity and the specific fungus responsible. The landscape of treatment options is diverse, offering solutions that range from topical applications to advanced laser therapy. Understanding these treatments in depth can guide individuals in choosing the most effective strategy for combating their fungal nail infections.
1. Topical Medications
Overview
Topical treatments involve the application of antifungal creams and ointments directly onto the infected nail. These medications are designed to penetrate the nail’s surface, reaching the fungus to halt its growth.
Application Process
- Regular, consistent application is critical, often extending over several months, to fully eradicate the fungus and allow a healthy nail to grow in its place.
- The treatment duration and frequency depend on the infection’s severity and the specific product used.
Options Available
- A wide range of antifungal topical treatments is available, from over-the-counter products to stronger, prescription-strength formulations.
- The choice between these options should be guided by a healthcare professional, based on the infection’s characteristics.
2. Oral Medications
Overview
Oral antifungal medications are systemic treatments that target the fungus from within the body. These are typically reserved for more severe cases or when topical treatments have been ineffective.
Treatment Regimen
- Patients must adhere strictly to the prescribed dosage and complete the entire course of medication to ensure the best outcomes.
- The duration of treatment can vary but often lasts several months to ensure the fungus is completely eradicated and healthy nail growth is supported.
3. Nail Removal
Overview
In cases where the infection is particularly severe or resistant to other forms of treatment, surgical removal of the nail may be considered. This procedure allows for direct treatment of the nail bed beneath.
Procedure and Follow-up
- Nail removal is generally seen as a last resort and is performed under local anesthesia.
- Following the removal, topical antifungal treatments are usually applied to the nail bed to treat the underlying infection.
4. Laser Treatment
Overview
Laser therapy represents a modern, non-invasive approach to fungal nail infection treatment. This method uses laser energy to directly target and destroy the fungal organisms without damaging the surrounding nail or skin.
Treatment Sessions
- Multiple laser treatment sessions may be required to fully address the infection, with the exact number depending on the infection’s extent and severity.
- Laser therapy has shown promising results, with many patients experiencing significant improvements in the appearance and health of their nails.
Home Remedies and Preventive Measures for Fungal nail infections
Home Care Practices for Healthy Feet
1. Prioritizing Foot Cleanliness and Dryness:
- Maintaining impeccable foot hygiene is paramount. This includes thoroughly washing your feet with soap and water daily, ensuring special attention is given to the spaces between the toes where moisture can accumulate.
- After washing, dry your feet completely with a clean towel. Consider using a hairdryer on a cool setting to ensure no moisture remains, as fungi thrive in moist environments.
2. Regular Nail Maintenance:
- Keep your nails trimmed and filed, removing any rough edges that could harbor fungi. Short, well-maintained nails are less likely to become infected and reduce the risk of spreading the infection to other nails.
- Disinfect your nail clippers and files after each use to prevent the spread of fungi.
3. Choosing the Right Footwear and Socks:
- Select shoes made of breathable materials, such as leather or canvas, to allow air circulation around your feet, reducing the buildup of moisture.
- Wear moisture-wicking socks that draw sweat away from your skin, keeping your feet dry throughout the day. Change your socks daily, or more frequently if you have sweaty feet.
- Consider rotating your shoes regularly, giving them time to air out between wears.
4. Using Antifungal Products:
- Apply antifungal powders or sprays to your feet and inside your shoes to create an environment that’s inhospitable to fungal growth.
- These products can be particularly useful in the warmer months or if you’re engaged in activities that cause excessive sweating.
Preventive Measures to Avoid Fungal Infections
1. Protective Footwear in Public Areas:
- Always wear sandals or flip-flops when using public showers, locker rooms, or swimming pools. These areas are breeding grounds for fungi, and direct contact with the floor can increase your risk of infection.
2. Foot Hygiene Education:
- Educate yourself and your family about the importance of foot hygiene. Sharing knowledge on the causes and prevention of fungal infections can foster a healthy environment for everyone.
3. Regular Inspection of Feet and Nails:
- Regularly inspect your feet and nails for any signs of fungal infection, such as discoloration, thickening, or brittleness. Early detection can lead to more effective treatment and prevent the spread of the infection.
FAQ Section
Q: What are the main types of fungi causing nail infections? A: Fungal nail infections are primarily caused by dermatophytes, yeast, and molds, each affecting the nail in unique ways and requiring specific treatments.
Q: What are common causes of fungal nail infections? A: Key factors include poor foot hygiene, wearing tight-fitting shoes, and walking barefoot in public spaces like swimming pools or locker rooms.
Q: What symptoms should I look out for? A: Symptoms include yellow or white nail discoloration, thickening of the nails, brittle or crumbly texture, distorted nail shape, foul odor, and nail separation from the nail bed.
Q: How are fungal nail infections diagnosed? A: Diagnosis may involve a visual examination, microscopic examination of a nail sample, and possibly a culture test to identify the fungus type.
Q: What treatment options are available? A: Treatments range from topical and oral medications to nail removal and laser treatment, depending on the infection’s severity.
Conclusion
Fungal nail infections demand a comprehensive approach for effective management and eradication. By combining professional medical treatments with diligent home care and preventive strategies, individuals can significantly improve their nail health. Early detection, understanding the underlying causes, and adhering to prescribed treatments are key to overcoming this common yet treatable condition. Embrace these insights and strategies to embark on your journey toward fungal-free nails and enhanced well-being.







Great post.