Dive into our expert guide on Sesamoiditis, the under-toe pain affecting many. Learn about its causes, symptoms, and effective management strategies for lasting relief and improved foot health.

Introduction
Welcome to our in-depth exploration of Sesamoiditis, a condition that brings significant discomfort under the big toe, affecting your mobility and quality of life. This guide unpacks the intricacies of Sesamoiditis, from its causes and symptoms to a range of effective management strategies. Whether you’re an athlete, a dancer, or experiencing pregnancy-related foot changes, understanding Sesamoiditis is the first step towards finding relief and maintaining foot health during your daily activities.
Table of Contents
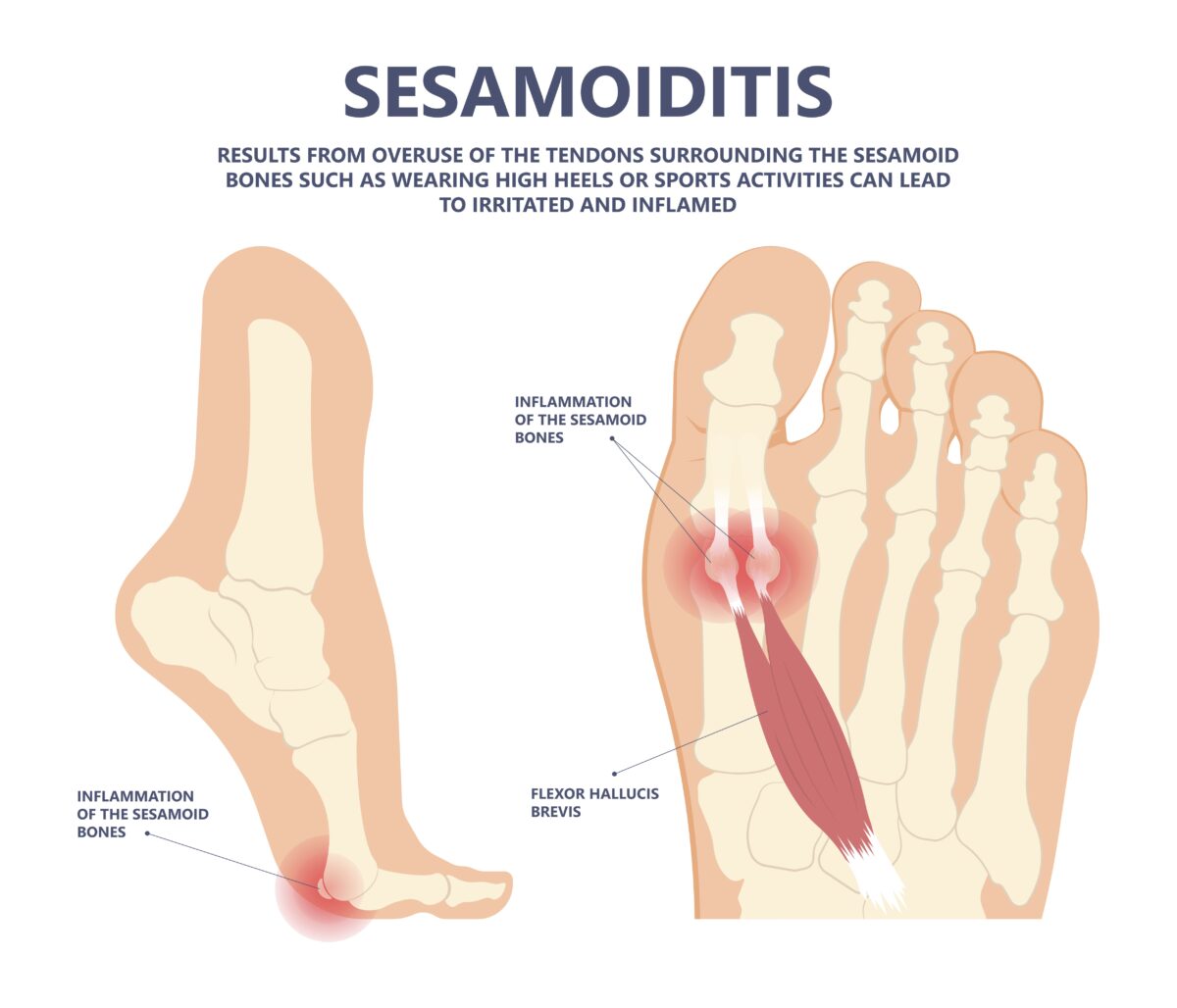
What is Sesamoiditis?
Sesamoiditis is a condition that can cause significant discomfort under your big toe, impacting your ability to walk, run, or even stand comfortably. This condition involves inflammation of the sesamoid bones, two small, pea-shaped bones located in the ball of your foot, beneath the big toe joint. These bones are embedded within tendons and act as a pulley system, providing leverage when you push off your toes while walking or running. Due to their location and function, they’re susceptible to inflammation and injury, leading to the painful condition known as sesamoiditis.
Primary Causes of Sesamoiditis

The root cause of sesamoiditis is often linked to repetitive activities that exert excessive force on the ball of the foot, including:
| High-Impact Sports: Activities such as running, basketball, and soccer, where intense footwork is involved, can place significant stress on the sesamoid bones. |
| Dance: Ballet dancers, in particular, face a high risk due to the frequent pressure applied to the forefoot while dancing on tiptoes. |
| Occupational Hazards: Jobs that require long periods of standing or walking can also contribute to the development of sesamoiditis. |

Contributing Factors
Beyond the direct causes, several factors can increase the likelihood of experiencing sesamoiditis, making some individuals more susceptible than others:
Improper Footwear: Shoes that lack proper support or have high heels can alter the foot’s natural alignment and pressure distribution, increasing the risk. Footwear with a narrow toe box that compresses the toes can also lead to sesamoiditis.
Foot Structure: Individuals with high arches may experience more force concentration on the ball of the foot, predisposing them to sesamoiditis. Similarly, flat feet or other structural foot abnormalities can disrupt normal foot mechanics, leading to increased stress on the sesamoid bones.
Pre-existing Foot Conditions: Conditions that alter the way weight is distributed across the foot, such as bunions or hammertoes, can also heighten the risk of developing sesamoiditis.
Symptoms to Watch For
Recognizing the symptoms of sesamoiditis early on is crucial for timely intervention and management of the condition. Here’s a closer look at the symptoms to be mindful of:

Pain Under the Big Toe
The most noticeable sign of sesamoiditis is a persistent pain located under the big toe, especially within the ball of the foot. This discomfort can start off mild and gradually worsen, becoming particularly pronounced during activities that place pressure on the forefoot, such as walking or running.
Swelling and Bruising
The area around the sesamoid bones may exhibit visible swelling or bruising as a result of inflammation. This can contribute to the discomfort felt and serve as a visual indicator of the condition.
Difficulty with Toe Movement
Sesamoiditis can impair your ability to bend and straighten the big toe. Movements that were once effortless may become challenging or painful, affecting your gait and overall foot function.
Warmth and Tenderness
You might notice a sensation of warmth or tenderness when touching the area under the big toe. This is indicative of inflammation and can help differentiate sesamoiditis from other foot conditions.
Pain with Specific Footwear or Barefoot Walking
Certain shoes, particularly those with inadequate support or high heels, can exacerbate the pain associated with sesamoiditis. Similarly, walking barefoot, especially on hard surfaces, may intensify the discomfort due to the lack of cushioning and support.
Navigating Sesamoiditis: From Diagnosis to Recovery
Sesamoiditis, characterized by pain under the big toe and in the ball of the foot, requires a careful and comprehensive approach for diagnosis and treatment. Here’s a closer look at how healthcare professionals diagnose this condition and the effective treatments available to manage and alleviate its symptoms.
Diagnosis
The process begins with a detailed examination by a healthcare provider, focusing on the foot’s structure, the specific location of the pain, and any activities that exacerbate the condition. To confirm a diagnosis of sesamoiditis and rule out other potential issues such as fractures, imaging tests are often utilized, including:
- X-rays: To provide a clear view of the bones and identify any abnormalities.
- MRIs: Offering detailed images of both bones and soft tissues, MRIs can help assess the extent of inflammation around the sesamoid bones.
Effective Treatment Strategies
Once sesamoiditis is diagnosed, the goal of treatment is to alleviate pain, reduce inflammation, and address any underlying issues contributing to the condition. Treatment plans typically include a combination of the following strategies:
- Rest and Ice Application: Taking a break from activities that put pressure on the foot and applying ice to the affected area can significantly reduce swelling and pain.
- Cushioned Pads or Orthotic Inserts: These devices can help redistribute pressure away from the sesamoid bones, providing relief from discomfort.
- Supportive Footwear: Shoes with a low heel and a wide toe box can minimize stress on the sesamoid bones. Avoiding high heels and opting for footwear with adequate cushioning and support is crucial.
- NSAIDs: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs can be effective in managing pain and reducing inflammation, offering temporary relief from symptoms.
- Physical Therapy: Tailored exercises designed to strengthen the muscles around the big toe and improve foot mechanics can help alleviate pain and prevent future issues.
- Immobilization: In cases where conservative treatments do not provide sufficient relief, immobilizing the foot with a brace or cast may be necessary to allow the area to heal.
- Surgery: As a last resort, surgical intervention may be considered to remove the sesamoid bone or repair damaged tendons, especially if other treatments fail to resolve the condition.
Prevention Strategies
Choose the Right Footwear
The foundation of sesamoiditis prevention lies in selecting shoes that offer proper support and comfort. For high-impact activities such as running, dancing, or sports, ensure your footwear provides adequate cushioning and has a wide toe box to minimize pressure on the forefoot. Avoid high heels or shoes with narrow toe areas that can exacerbate stress on the sesamoid bones.
Incorporate Foot-Strengthening Exercises
Regular exercises that strengthen the muscles of the feet can help maintain arch support and prevent conditions like sesamoiditis. Simple exercises such as toe curls, marble pickups, and arch lifts can be performed at home to enhance foot strength and flexibility.
Maintain a Healthy Weight
Excess body weight can increase the pressure and stress on your feet, particularly on the sesamoid bones. Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise can help alleviate unnecessary foot strain.
Stretch Regularly
Stretching the feet, ankles, and calves can improve flexibility and reduce the risk of injuries that might lead to sesamoiditis. Incorporate stretching into your daily routine, especially before and after exercise.
The Importance of Awareness
| Recognize the Symptoms |
| Early detection of sesamoiditis is crucial for effective management. Be vigilant for signs such as pain in the ball of the foot, swelling, difficulty in toe movement, or a sensation of walking on a pebble. |
| Seek Early Intervention |
| If you suspect sesamoiditis or experience persistent foot pain, consult a healthcare professional promptly. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent the condition from escalating and facilitate a faster recovery. |
| Educate Yourself and Others |
| Understanding the causes, risk factors, and preventive measures for sesamoiditis can empower you and those around you to take proactive steps toward foot health. Sharing knowledge and experiences can also help build a supportive community for those affected by foot conditions. |
Moving Forward
Dealing with sesamoiditis involves patience and adherence to a comprehensive treatment plan. By combining professional medical advice with self-care measures, individuals can effectively manage it’s symptoms and work towards a full recovery. It’s important to follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations closely and communicate any changes in your symptoms. With the right approach, it’s possible to return to your daily activities without the shadow of foot pain.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What exactly is Sesamoiditis?
A: Sesamoiditis is the inflammation of the sesamoid bones, located in the ball of your foot beneath the big toe joint, leading to pain and discomfort.
Q: What causes Sesamoiditis?
A: It’s often caused by repetitive activities that exert excessive force on the ball of the foot, improper footwear, and certain foot structures that predispose individuals to stress on the sesamoid bones.
Q: How can I tell if I have Sesamoiditis?
A: Key symptoms include persistent pain under the big toe, swelling, difficulty moving the toe, and discomfort when walking or wearing certain shoes.
Q: What are the best ways to manage Sesamoiditis?
A: Management includes rest, ice application, using orthotic inserts, wearing supportive footwear, engaging in physical therapy, and, in severe cases, considering surgical options.
Conclusion
Sesamoiditis, while challenging, doesn’t have to limit your life. With the right knowledge and approach, you can manage the condition effectively and minimize its impact on your daily activities. Embrace supportive footwear, consider orthotic solutions, and engage in targeted exercises to strengthen your feet. Remember, early intervention and consistent management are key to overcoming the discomfort of Sesamoiditis. If symptoms persist, consulting with a healthcare professional is crucial for a tailored approach to your foot health.